Painful Bladder Syndrome
What is it?
Painful bladder syndrome is also known as, “Interstitial Cystitis,” or, “IC.” It is a syndrome of urinary frequency and pain in the bladder which can feel like a urinary tract infection, but when the urine is tested, no infection is found. The symptoms can be similar with overactive bladder, but when you have IC, you usually feel extreme discomfort associated with storing urine in the bladder, and this is what prompts you to run to the bathroom. There is the sensation that if you eliminate the urine from the bladder, even if it is a small amount, it will relieve the discomfort. Then there is mild relief with urination, but the discomfort returns shortly after. In overactive bladder, the need to urinate is associated with a fear of leaking if you don’t run to the bathroom quickly, not because holding the urine is inherently painful.
Why does it happen?
While the causes of IC are not fully known, it is felt to be from a defect in the lining of the bladder that allows substances in the urine to feel caustic to the bladder, similar to the way it would feel if you poured salt water on an open wound. The bladder lining may become compromised as a result of a previous infection, or a reaction to a constituent in the urine such as a medication or something you ate or drank. Many IC patients will try to identify triggers that cause IC flares, such as acidic foods or drinks, or alcohol. In some patients, there may be nerve endings which are hypersensitive, or symptoms which flare in relation to emotional states and other types of problems related to the nervous system, such as irritable bowel syndrome.
What can I do about it?
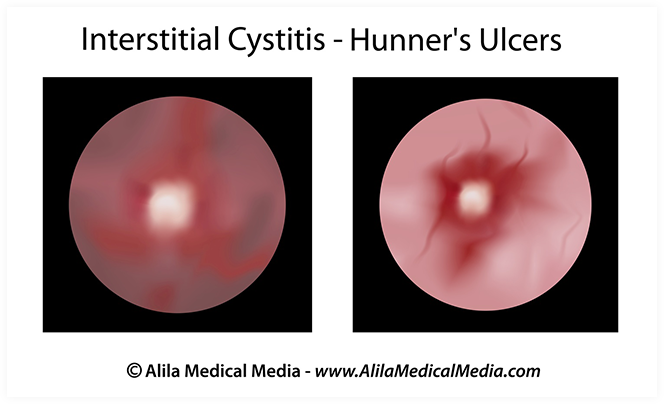
The treatment for IC is multifactorial, aimed at the pain symptoms as well as the frequency and urgency. If medications are not effective, we will usually instill medication into your bladder in the office. If this helps, we will schedule you for repeat instillations, or set you up to be able to do them on your own at home. In many cases, Dr. Kumar will perform a cystoscopy to rule out any other issues in the bladder, and check for the presence of Hunner’s ulcers and glomerulations in the bladder. These are areas where the bladder tissue is clearly unhealthy, scarred and friable, meaning it bleeds very easily on distention of the bladder. Dr. Kumar may recommend a biopsy to rule out other pathology. If you do have Hunner’s ulcers, Dr. Kumar may recommend a procedure to inject a steroid underneath the unhealthy tissue.
Often with IC patients, we try different treatments until we find one that works. It is helpful to know which patients have Hunner’s ulcers because direct treatment of the bladder can be very helpful for these patients. Dr. Kumar will offer you treatment options to maximize relief from your symptoms.


 / 53 Reviews
/ 53 Reviews
